Dissecting the Intricacies of Continuously Variable Transmission
Imagine cruising down an open highway at high speed, with your car smoothly transitioning between gears without you even noticing. This is the magic of Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT), an innovation that's redefining the way we drive. The concept of CVT is not a new one. Leonardo da Vinci, the Renaissance man himself, first sketched a stepless continuously variable transmission in 1490. However, it wasn't until the 20th century that CVT made its way into the automotive world. DAF, a Dutch automaker, introduced the first commercially successful CVT in their small car, the DAF 600, in 1958. CVT's appeal lies in its simplicity and efficiency. Unlike traditional automatic or manual transmissions, which have a set number of gear ratios, a CVT can theoretically operate at an infinite number of gear ratios. This allows the engine to run at its most efficient speed, regardless of how fast the car is going.
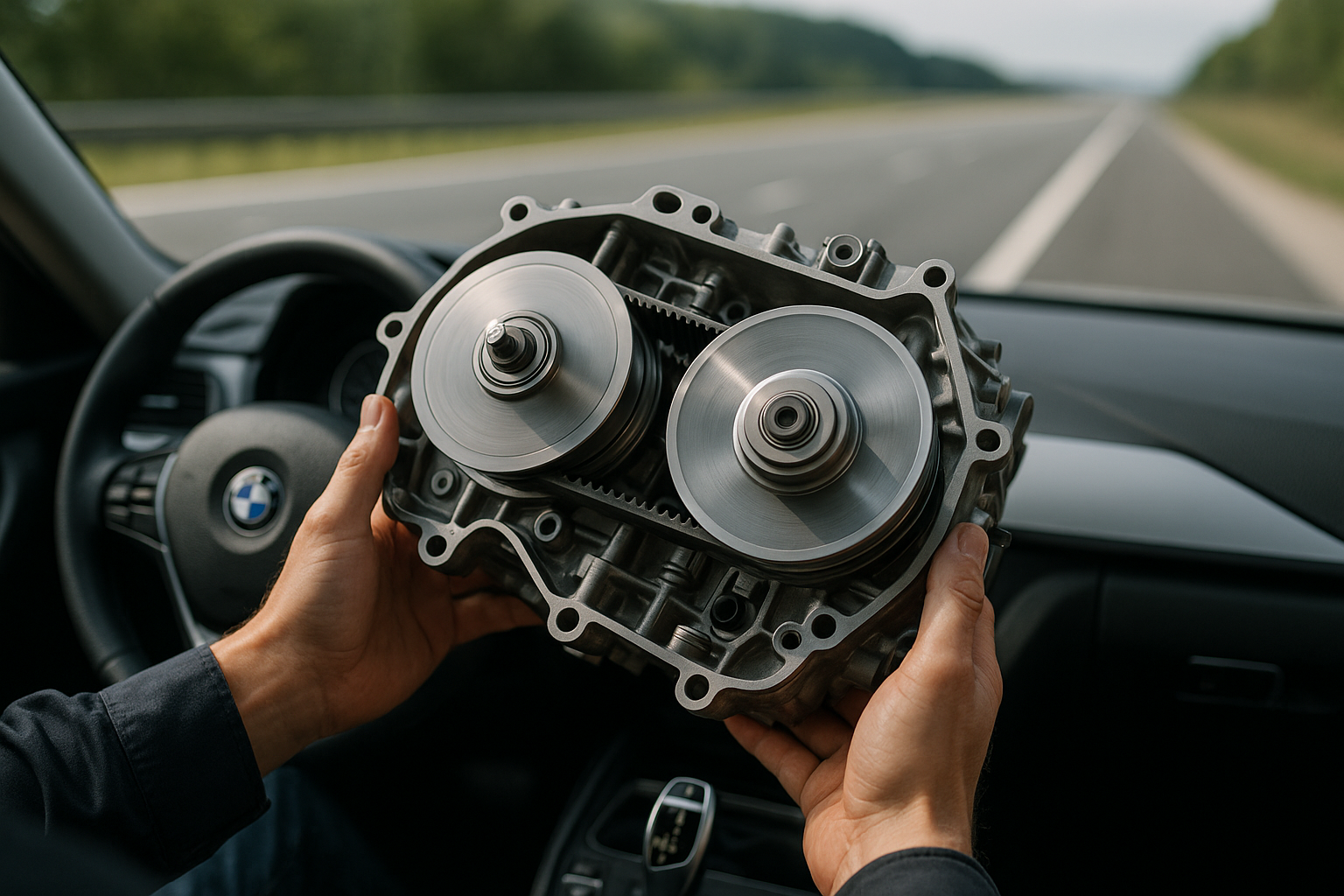

CVT: A Game Changer in Today’s Automotive Industry
The use of CVT has surged in the past decade, thanks to its fuel efficiency and smooth operation. With environmental concerns becoming more pressing, the industry is turning to CVT as a way to reduce emissions and improve fuel economy. Many manufacturers, including Nissan, Subaru, and Honda, have embraced CVT in their vehicles. Meanwhile, it’s not just limited to passenger cars. CVT is also finding its way into heavier vehicles like buses and trucks, where its efficiency can make a significant impact on fuel costs.
The Mechanics of Continuously Variable Transmission
CVT operates on a simple principle. It uses two pulleys connected by a belt, with one pulley connected to the engine and the other to the wheels. The diameter of these pulleys can change in response to the car’s needs, creating a wide range of possible gear ratios. This is what makes the transition between gears virtually seamless. Unlike a traditional transmission, which shifts gears abruptly, a CVT can change its gear ratios continuously, providing a smooth, uninterrupted driving experience.
Pros and Cons of CVT
The benefits of CVT are clear: improved fuel efficiency, smoother ride, and less maintenance due to fewer moving parts. However, it’s not without its challenges. Critics of CVT often point to its lackluster performance feel, as it lacks the defined gear shifts that enthusiasts enjoy. There’s also a perception that CVTs are not as durable as traditional transmissions, although this is largely a myth. With proper maintenance, a CVT can last just as long as a conventional transmission.
Looking Ahead: The Future of CVT
Despite some criticisms, the future of CVT looks bright. As manufacturers continue to prioritize fuel efficiency and emissions reductions, the demand for CVT is likely to grow. Advances in technology are also helping to overcome some of the drawbacks of CVT. For instance, some manufacturers are now programming “virtual” gear shifts into their CVTs, giving drivers the feel of a traditional transmission. As we move forward, the unique benefits and adaptability of CVT will continue to make it a vital player in the automotive industry.
In conclusion, Continuously Variable Transmission is an intriguing facet of automotive technology, offering a unique blend of efficiency and smooth operation. As the industry continues to evolve, CVT is poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of driving.